atomic orbitals
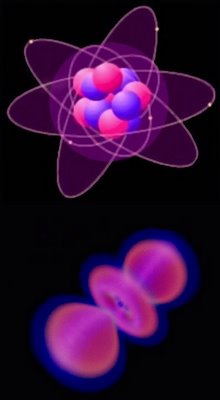
Atomic orbitals are often represented as electrons spinning around the nucleus (top - carbon). However, orbital shells actually represent the volume in which the wave-form electron is likeliest to be found (shaded).
As such, orbitals are more akin to a cloud around the nucleus (bottom - sp hybrid hydrogen).
The location of electrons within orbitals is described mathematically by the Schrodinger equations. Computer simulations reveal probability distributions for orbitals.
Table of images of orbitals / Scatter plot of probabilities / interactive / virtual text / virtual text orbitals / download audio-anim of H2 bonding / audio-anim of hybridization of s p orbitals / voxel movie of orbital / movie 2 / movie 3 / movie 4 /
Atomic orbitals are distorted in molecular covalent bonds, where atoms share electrons within a molecule.
When electrons are shared between two atoms of the same element, the electrons are shared equally, creating a non-polar covalent bond.
When electrons are shared between atoms of different elements, the electrons are not shared equally. Unequal sharing results in a polar covalent bond in which the increased-probability cloud over one atom has a slightly negative charge compared to a slightly positive charge over the other -- a dipole.
12/31/2006
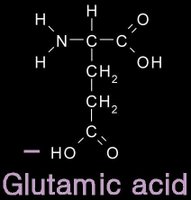
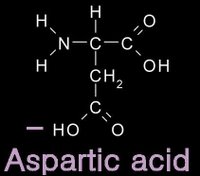
12/31/2006 11:50:00 PM 0 commentsacidic and basic amino acids
Several amino acids possess a side chain that adopts a + (basic) or - (acidic) charge at the pH of cells.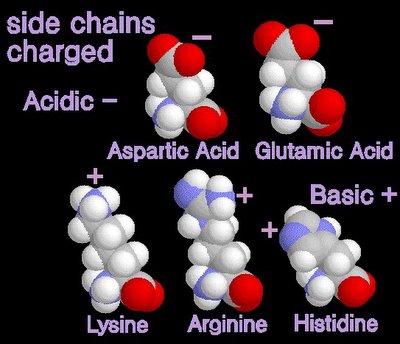 grey - carbon / white - hydrogen / blue - nitrogen / red - oxygen
grey - carbon / white - hydrogen / blue - nitrogen / red - oxygen
 grey - carbon / white - hydrogen / blue - nitrogen / red - oxygen
grey - carbon / white - hydrogen / blue - nitrogen / red - oxygenpolar amino acids
When electrons are shared between atoms of different elements, the electrons are not shared equally, resulting in a polar bond in which the increased-probability cloud over one atom has a slightly negative charge (delta -)while that over the other atom has a slightly positive charge (delta +). This unequal sharing generates a dipole. Molecules with dipoles tend to align positive toward negative.
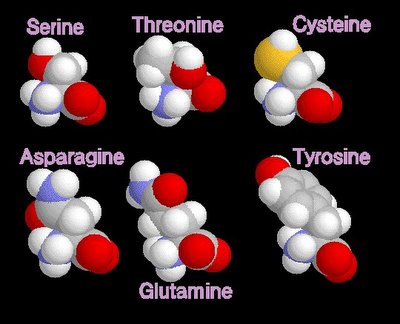 grey - carbon / white - hydrogen / blue - nitrogen / red - oxygen / yellow - sulphur
grey - carbon / white - hydrogen / blue - nitrogen / red - oxygen / yellow - sulphur
 grey - carbon / white - hydrogen / blue - nitrogen / red - oxygen / yellow - sulphur
grey - carbon / white - hydrogen / blue - nitrogen / red - oxygen / yellow - sulphur
non-polar amino acids
When electrons are shared between two atoms of the same element, the electrons are shared equally, creating a non-polar bond.
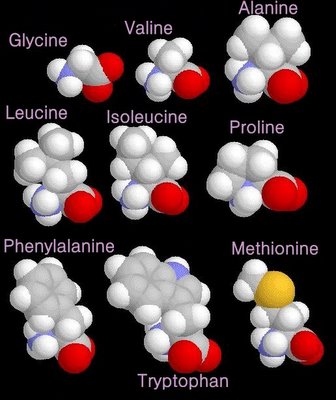 grey - carbon / white - hydrogen / blue - nitrogen / red - oxygen / yellow - sulphur
grey - carbon / white - hydrogen / blue - nitrogen / red - oxygen / yellow - sulphur
 grey - carbon / white - hydrogen / blue - nitrogen / red - oxygen / yellow - sulphur
grey - carbon / white - hydrogen / blue - nitrogen / red - oxygen / yellow - sulphurglycerol
Glycerol is a three carbon substance that is important component of triglycerides (i.e. fats and oils) and of phospholipids. Glycerol forms the backbone of fatty acids in triglycerides.